pacman::p_load(spdep, tmap, sf, knitr, tidyverse)Hands-on_Ex2_Spatial_Weights
The Study Area and Data
Two data sets will be used in this hands-on exercise:
- Hunan County Boundary Layer: Geospatial data set in ESRI shapefile format
- Hunan_2012.csv: Selected local development indicators in 2012
Getting started
We will use the p_load() function of the pacman package to load the required packages: spdep (for spatial weights), sf, tmap, and tidyverse.
Getting the Data into the R Environment
Import Shapefile into R Environment
st_read() can be used to import the Hunan shapefile into a sf dataframe
hunan <- st_read(dsn = 'data/geospatial',
layer = 'Hunan')Reading layer `Hunan' from data source
`D:\phlong2023\ISSS624\Hands-on_Ex\Hands-on_Ex2\data\geospatial'
using driver `ESRI Shapefile'
Simple feature collection with 88 features and 7 fields
Geometry type: POLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 108.7831 ymin: 24.6342 xmax: 114.2544 ymax: 30.12812
Geodetic CRS: WGS 84Import Attribute Data (aspatial) into R Environment
read_csv() can be used to import the Hunan_2012.csv into R as a data frame
hunan2012 <- read_csv('data/aspatial/Hunan_2012.csv')Performing Relational Join
Since both data frames have 88 rows and share the ‘County’ column, we can use left_join() to update the hunan sf data frame with with attribute fields of hunan2012 data frame.
hunan <- left_join(hunan, hunan2012) %>%
select(1:4, 7, 15)The left_join() argument automatically seeks out the shared field for joining. In this case, it is ‘by = join_by(County)’.
Visualizing Regional Development Indicator
we can prepare a basemap and a choropleth map showing the distribution of GDPPC 2012 by using qtm() of the tmap package.
basemap <- tm_shape(hunan)+
tm_polygons() +
tm_text('NAME_3', size = 0.3) #A basemap is created showing the boundaries and names of counties in Hunan
gdppc <- qtm(hunan, 'GDPPC') # A choropleth map showing the distribution of GDPPC in Hunan
tmap_arrange(basemap, gdppc, asp = 1, ncol = 2) # Arranging basemap and gdppc along two columns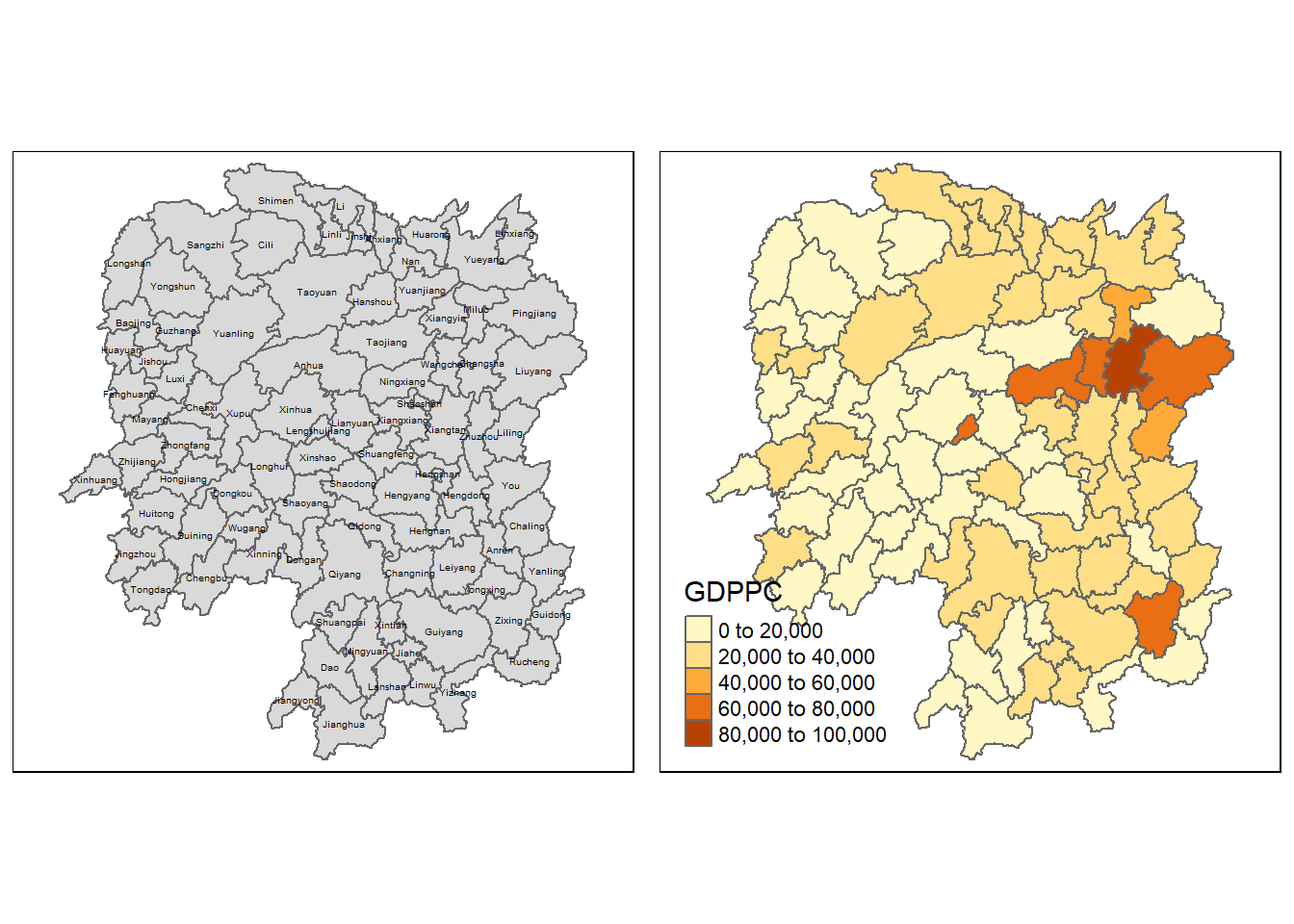
Computing Contiguity Spatial Weights
We can use poly2nb() of spep to compute contiguity weight matrices for the study area. This function builds a neighbours list based on regions with contiguous boundaries.
In poly2nb(), you can pass TRUE or FALSE to the queen argument in order to indicate whether to use the queen method. The default is TRUE.
Computing (QUEEN) contiguity based neighbours
wm_q <- poly2nb(hunan, queen = TRUE)
summary(wm_q)Neighbour list object:
Number of regions: 88
Number of nonzero links: 448
Percentage nonzero weights: 5.785124
Average number of links: 5.090909
Link number distribution:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11
2 2 12 16 24 14 11 4 2 1
2 least connected regions:
30 65 with 1 link
1 most connected region:
85 with 11 linksThe summary report above shows that there are 88 area units in Hunan. The most connected area unit has 11 neighbours (area 85). There are two area units with only 1 neighbour (30 and 65).
For each polygon in our polygon object, wm_q lists all neighboring polygons. To see the neighbors for the first polygon in the object, you can specify it similar to a list of list
wm_q[[1]][1] 2 3 4 57 85Polygon 1 has 5 neighbors. The numbers represent the polygon IDs as stored in hunan spdf class
We can retrieve the county name of Polygon ID = 1 by specifying it its position in the hunan data fram
hunan$County[1][1] "Anxiang"Similarly, you can extract the name of its neighbors using their Polygon ID in wm_q
hunan$County[c(2,3,4,57,85)][1] "Hanshou" "Jinshi" "Li" "Nan" "Taoyuan"We can also retreive the GDPPC of these five counties
nb1 <- wm_q[[1]]
nb1_gdppc <- hunan$GDPPC[nb1]
nb1_gdppc[1] 20981 34592 24473 21311 22879Additionally, you can display the complete neighbor list using str() However, this output will cut across several pages.
Creating (ROOK) Contiguity Based Neighbours
We can use Rook contiguity instead of Queen contiguity by passing FALSE to the queen argument of poly2nb
wm_r <- poly2nb(hunan, queen = FALSE)
summary(wm_r)Neighbour list object:
Number of regions: 88
Number of nonzero links: 440
Percentage nonzero weights: 5.681818
Average number of links: 5
Link number distribution:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
2 2 12 20 21 14 11 3 2 1
2 least connected regions:
30 65 with 1 link
1 most connected region:
85 with 10 linksSimilar to Queen, the number of area units in Hunan remains unchanged at 88. However, the most connected area unit has only 10 neighbours (area 85). The two area units with only one neighbour remain the same (area 30 and 65).
Visualizing Contiguity Weights
A connectivity graph takes a point and displays a line to each neighboring point.
We are working with polygons at the moment, so we will need to get points in order to make our connectivity graphs. The most typical method for this will be polygon centroids.
We can use the sf package to get Latitude and Longitude of polygon centroids before moving onto the graphs.
We will need points to associate with each polygon before we can make our connectivity graph. It will be a little more complicated than just running st_centroid on the sf object. We need the coordinates in a separate data frame. To do this we will use a mapping function.
The mapping function applies a given function to each element of a vector and returns a vector of the same length. Our input vector will be the geometry column of hunan. Our function will be st_centroid. We will be using map_dbl() variation of map from thhe purrr package.
To get our longitude values, we map the st_centroid function over the geometry column of hunan and access the longitude value through double bracket notation [[]] and 1 ([[1]]]). This allows us to get only the longitude, which is the first value in each centroid.
longitude <- map_dbl(hunan$geometry, ~st_centroid(.x)[[1]])We can do the same for latitude, only with [[2]] instead.
latitude <- map_dbl(hunan$geometry, ~st_centroid(.x)[[2]])Now that we have longitude and latitude, we can use cbind to put them together into the same object (coords) as two separate columns
coords_hunan <- cbind(longitude, latitude)We can check the first few observation of this new object using head()
head(coords_hunan) longitude latitude
[1,] 112.1531 29.44362
[2,] 112.0372 28.86489
[3,] 111.8917 29.47107
[4,] 111.7031 29.74499
[5,] 111.6138 29.49258
[6,] 111.0341 29.79863Plotting Queen Contiguity Based Neighbours Map
The contiguity map will draw a line between the centroid of each polygon and the centroids of its neighbors based on the Queen Contiguity.
plot(hunan$geometry, border = 'lightgrey')
plot(wm_q,coords_hunan, pch = 19, cex = 0.6, add = TRUE, col = 'red')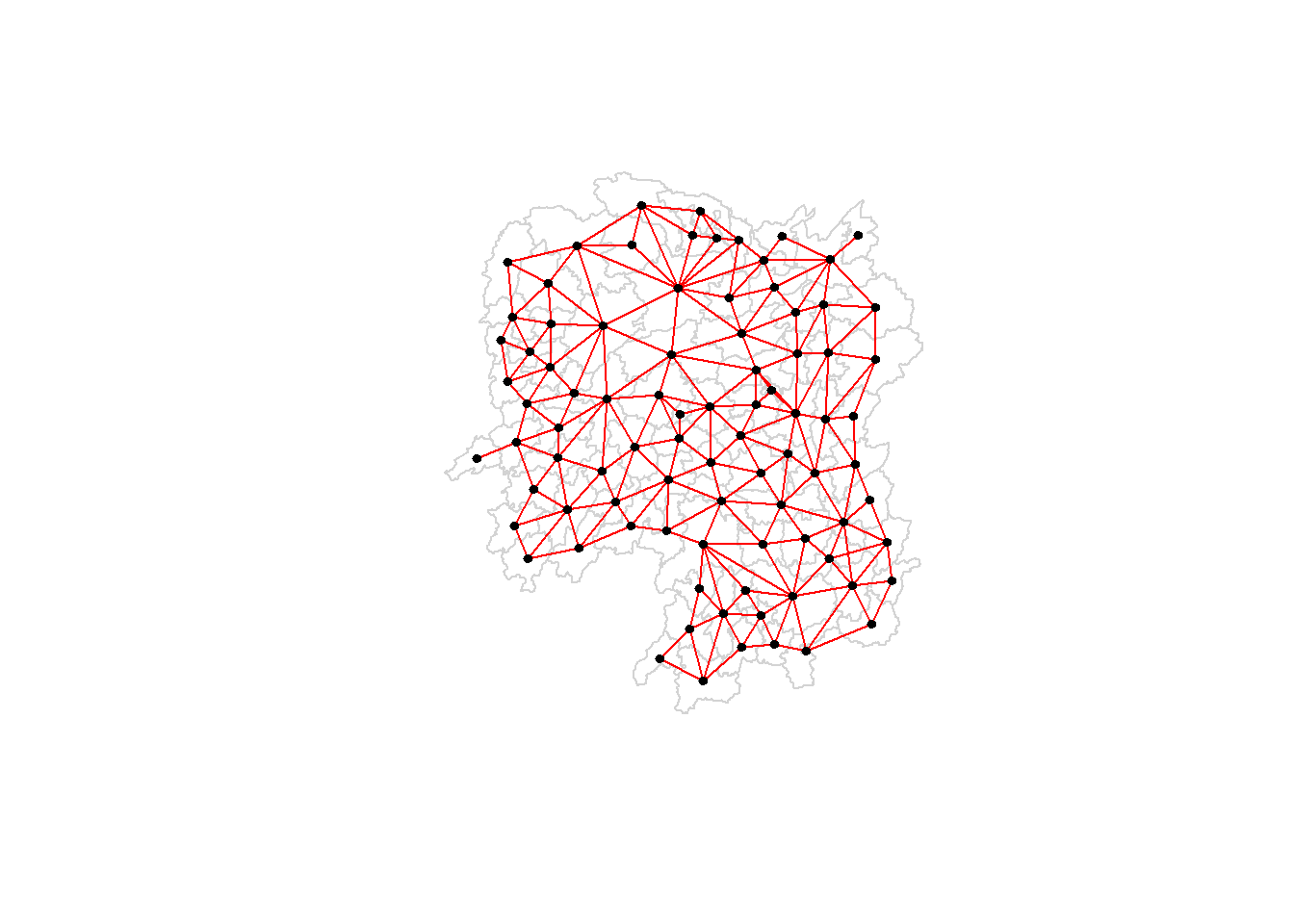
If we use plot(wm_q, coords_hunan) by itself, it will only provide a contiguity map with no border for each county.
Plotting Rook Contiguity Based Neighbours Map
We can easily make a Rook contiguity map instead of a Queen contiguity map by using wm_r instead of wm_q
plot(hunan$geometry, border = 'lightgrey')
plot(wm_r, coords_hunan, pch = 19, cex = 0.6, add = TRUE, col = 'red')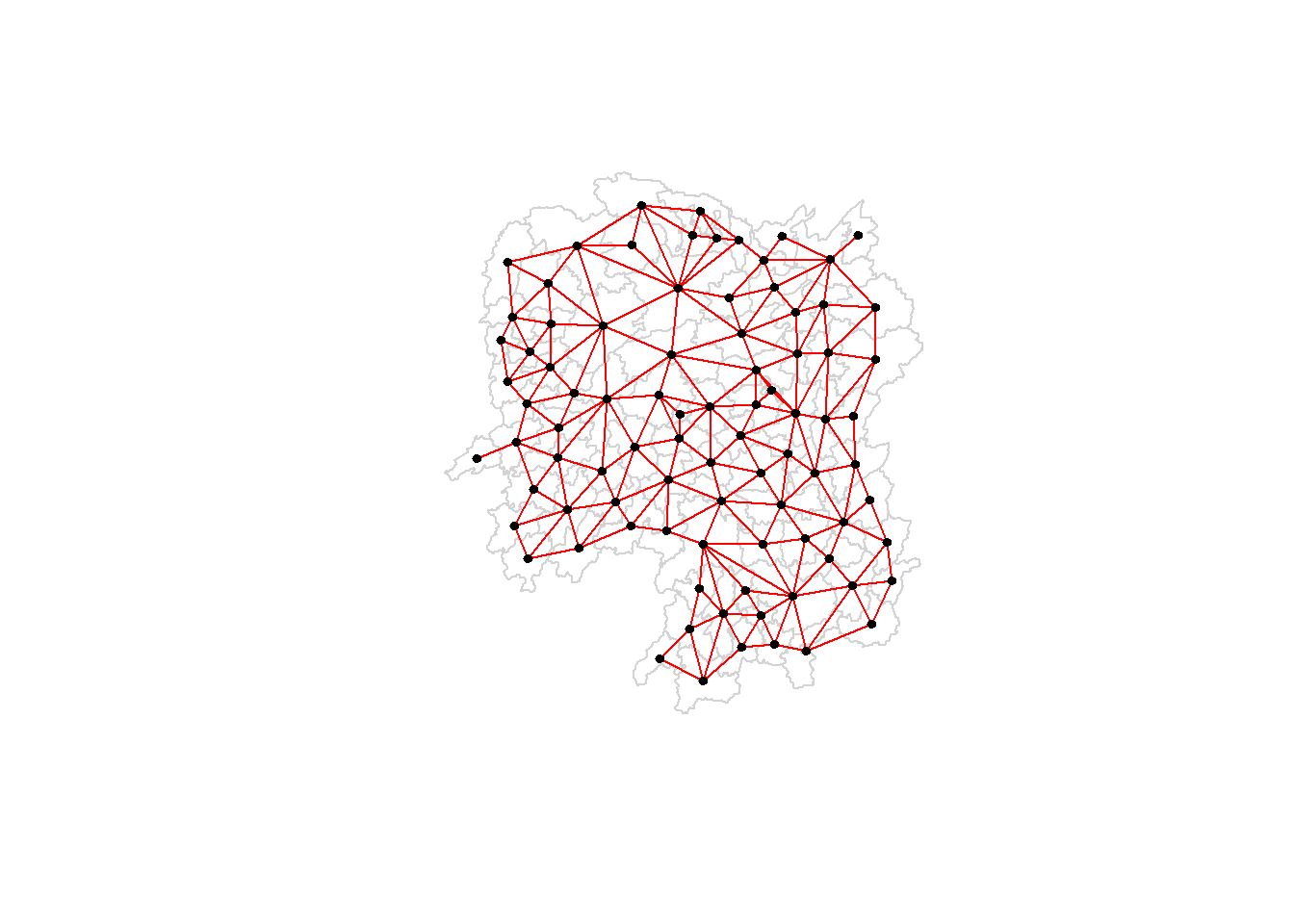
Plotting both Queen and Rook Contiguity Based Neighbours Maps
par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(hunan$geometry, main = 'Queen Contiguity', border = 'lightgrey')
plot(wm_q, coords_hunan, pch = 19, cex = 0.6, add = TRUE, col = 'red')
plot(hunan$geometry, main = 'Rook Contiguity', border = 'lightgrey')
plot(wm_r, coords_hunan, pch = 19, cex = 0.6, add = TRUE, col = 'red')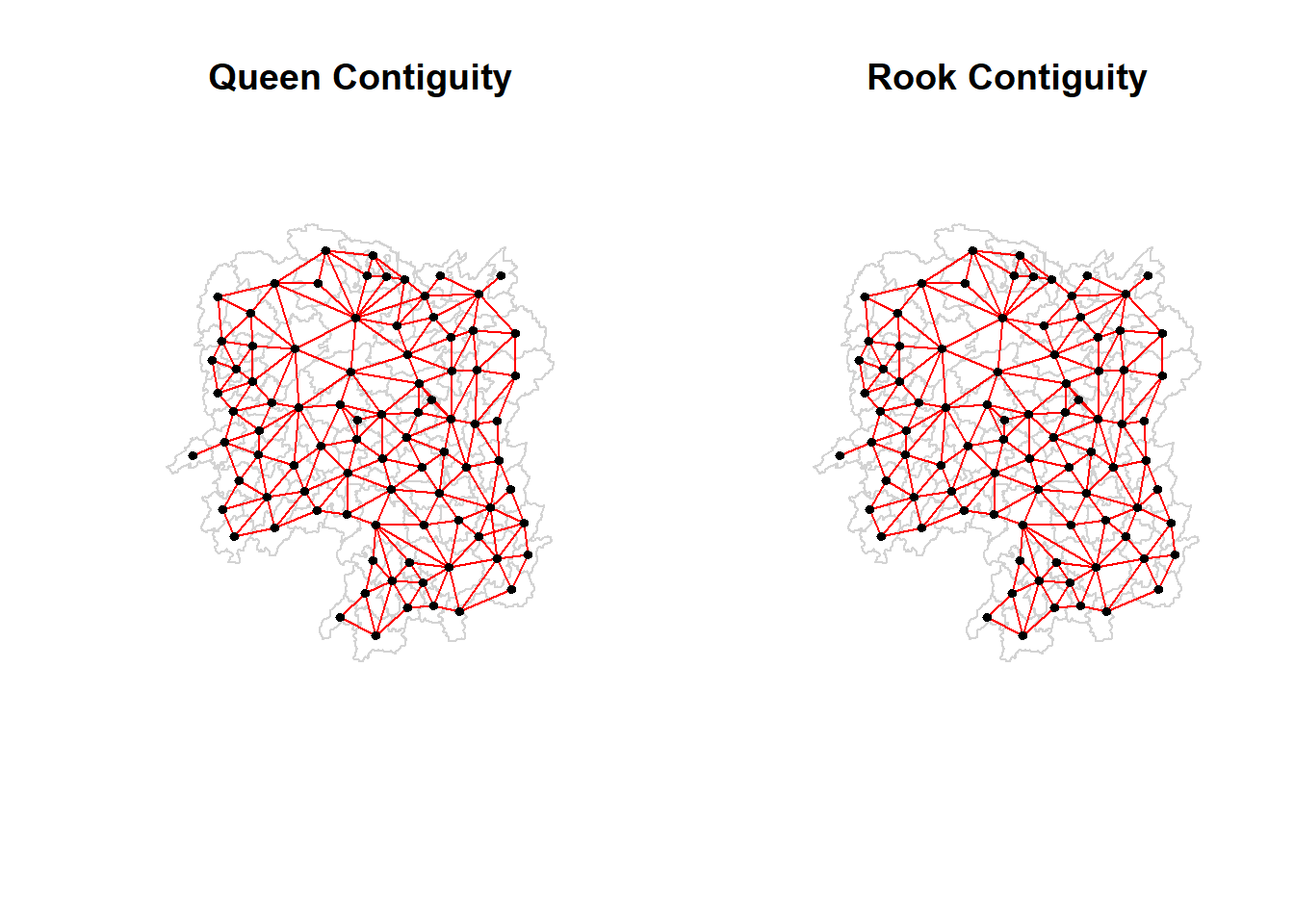
Computing Distance Based Neighbours
Distance-based weight matrices can be derived using dnearneigh() of spdep.
The function identifies neighbours of region points by Euclidean distance with a distance band with lower d1= and upper d2= bounds controlled by the bounds= argument.
If unprojected coordinates are used and either specified in the coordinates object x or with x as a two column matrix and longlat = TRUE, great circle distances in km will be calculated assuming the WGS84 reference ellipsoid.
Determine the Cut-off Distance
First, we need to determine the upper limit for distance band by using the steps below:
Return a matrix with the indices of points belonging to the set of the k nearest neighbours of each other by using knearneigh() of sdpep
Convert the k nearest neighbour object returned by knearneigh() into a neighbours list of class nb with a list of integer vectors containing neighbour region number ids by using knn2nb()
Return the length of neighbour relationship edges by using nbdist() of spdep. The function returns in the units of the coordinates if the coordinates are projected, in km otherwise.
Remove the list structure of the returned object by using unlist().
k1 <- knn2nb(knearneigh(coords_hunan))
k1dists <- unlist(nbdists(k1, coords_hunan, longlat = TRUE))
summary(k1dists) Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
24.79 32.57 38.01 39.07 44.52 61.79 The summary report shows that the largest first nearest neighbour distance is 61.79 km, so using this as the upper threshold gives certainty that all units will have at least one neighbour.
Computing Fixed Distance Weight Watrix
dnearneigh() can be used to compute the distance weight matrix. It will create an object containing the neighbors of a each id based on their distance in km with a lower bound d1=0 and upper bound d2=62
wm_d62 <- dnearneigh(coords_hunan, 0, 62, longlat = TRUE)
wm_d62Neighbour list object:
Number of regions: 88
Number of nonzero links: 324
Percentage nonzero weights: 4.183884
Average number of links: 3.681818 str() can be used to display the content of wm_d62
str(wm_d62)List of 88
$ : int [1:5] 3 4 5 57 64
$ : int [1:4] 57 58 78 85
$ : int [1:4] 1 4 5 57
$ : int [1:3] 1 3 5
$ : int [1:4] 1 3 4 85
$ : int 69
$ : int [1:2] 67 84
$ : int [1:4] 9 46 47 78
$ : int [1:4] 8 46 68 84
$ : int [1:4] 16 22 70 72
$ : int [1:3] 14 17 72
$ : int [1:5] 13 60 61 63 83
$ : int [1:4] 12 15 60 83
$ : int [1:2] 11 17
$ : int 13
$ : int [1:4] 10 17 22 83
$ : int [1:3] 11 14 16
$ : int [1:3] 20 22 63
$ : int [1:5] 20 21 73 74 82
$ : int [1:5] 18 19 21 22 82
$ : int [1:6] 19 20 35 74 82 86
$ : int [1:4] 10 16 18 20
$ : int [1:3] 41 77 82
$ : int [1:4] 25 28 31 54
$ : int [1:4] 24 28 33 81
$ : int [1:4] 27 33 42 81
$ : int [1:2] 26 29
$ : int [1:6] 24 25 33 49 52 54
$ : int [1:2] 27 37
$ : int 33
$ : int [1:2] 24 36
$ : int 50
$ : int [1:5] 25 26 28 30 81
$ : int [1:3] 36 45 80
$ : int [1:6] 21 41 46 47 80 82
$ : int [1:5] 31 34 45 56 80
$ : int [1:2] 29 42
$ : int [1:3] 44 77 79
$ : int [1:4] 40 42 43 81
$ : int [1:3] 39 45 79
$ : int [1:5] 23 35 45 79 82
$ : int [1:5] 26 37 39 43 81
$ : int [1:3] 39 42 44
$ : int [1:2] 38 43
$ : int [1:6] 34 36 40 41 79 80
$ : int [1:5] 8 9 35 47 86
$ : int [1:5] 8 35 46 80 86
$ : int [1:5] 50 51 52 53 55
$ : int [1:4] 28 51 52 54
$ : int [1:6] 32 48 51 52 54 55
$ : int [1:4] 48 49 50 52
$ : int [1:6] 28 48 49 50 51 54
$ : int [1:2] 48 55
$ : int [1:5] 24 28 49 50 52
$ : int [1:4] 48 50 53 75
$ : int 36
$ : int [1:5] 1 2 3 58 64
$ : int [1:5] 2 57 64 66 68
$ : int [1:3] 60 87 88
$ : int [1:4] 12 13 59 61
$ : int [1:5] 12 60 62 63 87
$ : int [1:4] 61 63 77 87
$ : int [1:5] 12 18 61 62 83
$ : int [1:4] 1 57 58 76
$ : int 76
$ : int [1:5] 58 67 68 76 84
$ : int [1:2] 7 66
$ : int [1:4] 9 58 66 84
$ : int [1:2] 6 75
$ : int [1:3] 10 72 73
$ : int [1:2] 73 74
$ : int [1:3] 10 11 70
$ : int [1:4] 19 70 71 74
$ : int [1:5] 19 21 71 73 86
$ : int [1:2] 55 69
$ : int [1:3] 64 65 66
$ : int [1:3] 23 38 62
$ : int [1:2] 2 8
$ : int [1:4] 38 40 41 45
$ : int [1:5] 34 35 36 45 47
$ : int [1:5] 25 26 33 39 42
$ : int [1:6] 19 20 21 23 35 41
$ : int [1:4] 12 13 16 63
$ : int [1:4] 7 9 66 68
$ : int [1:2] 2 5
$ : int [1:4] 21 46 47 74
$ : int [1:4] 59 61 62 88
$ : int [1:2] 59 87
- attr(*, "class")= chr "nb"
- attr(*, "region.id")= chr [1:88] "1" "2" "3" "4" ...
- attr(*, "call")= language dnearneigh(x = coords_hunan, d1 = 0, d2 = 62, longlat = TRUE)
- attr(*, "dnn")= num [1:2] 0 62
- attr(*, "bounds")= chr [1:2] "GE" "LE"
- attr(*, "nbtype")= chr "distance"
- attr(*, "sym")= logi TRUEAnother way to display the structure of the weight matrix is to combine table() and card() of spdep
table(hunan$County, card(wm_d62))
1 2 3 4 5 6
Anhua 1 0 0 0 0 0
Anren 0 0 0 1 0 0
Anxiang 0 0 0 0 1 0
Baojing 0 0 0 0 1 0
Chaling 0 0 1 0 0 0
Changning 0 0 1 0 0 0
Changsha 0 0 0 1 0 0
Chengbu 0 1 0 0 0 0
Chenxi 0 0 0 1 0 0
Cili 0 1 0 0 0 0
Dao 0 0 0 1 0 0
Dongan 0 0 1 0 0 0
Dongkou 0 0 0 1 0 0
Fenghuang 0 0 0 1 0 0
Guidong 0 0 1 0 0 0
Guiyang 0 0 0 1 0 0
Guzhang 0 0 0 0 0 1
Hanshou 0 0 0 1 0 0
Hengdong 0 0 0 0 1 0
Hengnan 0 0 0 0 1 0
Hengshan 0 0 0 0 0 1
Hengyang 0 0 0 0 0 1
Hongjiang 0 0 0 0 1 0
Huarong 0 0 0 1 0 0
Huayuan 0 0 0 1 0 0
Huitong 0 0 0 1 0 0
Jiahe 0 0 0 0 1 0
Jianghua 0 0 1 0 0 0
Jiangyong 0 1 0 0 0 0
Jingzhou 0 1 0 0 0 0
Jinshi 0 0 0 1 0 0
Jishou 0 0 0 0 0 1
Lanshan 0 0 0 1 0 0
Leiyang 0 0 0 1 0 0
Lengshuijiang 0 0 1 0 0 0
Li 0 0 1 0 0 0
Lianyuan 0 0 0 0 1 0
Liling 0 1 0 0 0 0
Linli 0 0 0 1 0 0
Linwu 0 0 0 1 0 0
Linxiang 1 0 0 0 0 0
Liuyang 0 1 0 0 0 0
Longhui 0 0 1 0 0 0
Longshan 0 1 0 0 0 0
Luxi 0 0 0 0 1 0
Mayang 0 0 0 0 0 1
Miluo 0 0 0 0 1 0
Nan 0 0 0 0 1 0
Ningxiang 0 0 0 1 0 0
Ningyuan 0 0 0 0 1 0
Pingjiang 0 1 0 0 0 0
Qidong 0 0 1 0 0 0
Qiyang 0 0 1 0 0 0
Rucheng 0 1 0 0 0 0
Sangzhi 0 1 0 0 0 0
Shaodong 0 0 0 0 1 0
Shaoshan 0 0 0 0 1 0
Shaoyang 0 0 0 1 0 0
Shimen 1 0 0 0 0 0
Shuangfeng 0 0 0 0 0 1
Shuangpai 0 0 0 1 0 0
Suining 0 0 0 0 1 0
Taojiang 0 1 0 0 0 0
Taoyuan 0 1 0 0 0 0
Tongdao 0 1 0 0 0 0
Wangcheng 0 0 0 1 0 0
Wugang 0 0 1 0 0 0
Xiangtan 0 0 0 1 0 0
Xiangxiang 0 0 0 0 1 0
Xiangyin 0 0 0 1 0 0
Xinhua 0 0 0 0 1 0
Xinhuang 1 0 0 0 0 0
Xinning 0 1 0 0 0 0
Xinshao 0 0 0 0 0 1
Xintian 0 0 0 0 1 0
Xupu 0 1 0 0 0 0
Yanling 0 0 1 0 0 0
Yizhang 1 0 0 0 0 0
Yongshun 0 0 0 1 0 0
Yongxing 0 0 0 1 0 0
You 0 0 0 1 0 0
Yuanjiang 0 0 0 0 1 0
Yuanling 1 0 0 0 0 0
Yueyang 0 0 1 0 0 0
Zhijiang 0 0 0 0 1 0
Zhongfang 0 0 0 1 0 0
Zhuzhou 0 0 0 0 1 0
Zixing 0 0 1 0 0 0n_comp <- n.comp.nb(wm_d62)
n_comp$nc[1] 1table(n_comp$comp.id)
1
88 Plotting Fixed Distance Weight Matrix
We can plot the distance weight matrix using the code chunk below
plot(hunan$geometry, border = 'lightgrey')
plot(wm_d62, coords_hunan, add = TRUE) #add centroids and links between neighbors
plot(k1, coords_hunan, add = TRUE, col = 'red', length = 0.08) #add red coloration to the nearest neighbor based on distance
The red lines show the links of 1st nearest neighbours and the black lines show the links of neighbours within the cut-off distance of 62km.
Alternatively, we can plot two separate plots next to each other, one with centroid for each region and the links to all its neighbors, and one with centroid for each region and the link to its 1st nearest neighbor.
par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(hunan$geometry, border = 'lightgrey', main = '1st Nearest Neighbor')
plot(k1, coords_hunan, add = TRUE, col = 'red', length = 0.08)
plot(hunan$geometry, border = 'lightgrey', main = 'Distance Link')
plot(wm_d62, coords_hunan, add = TRUE, pch = 19, cex = 0.6)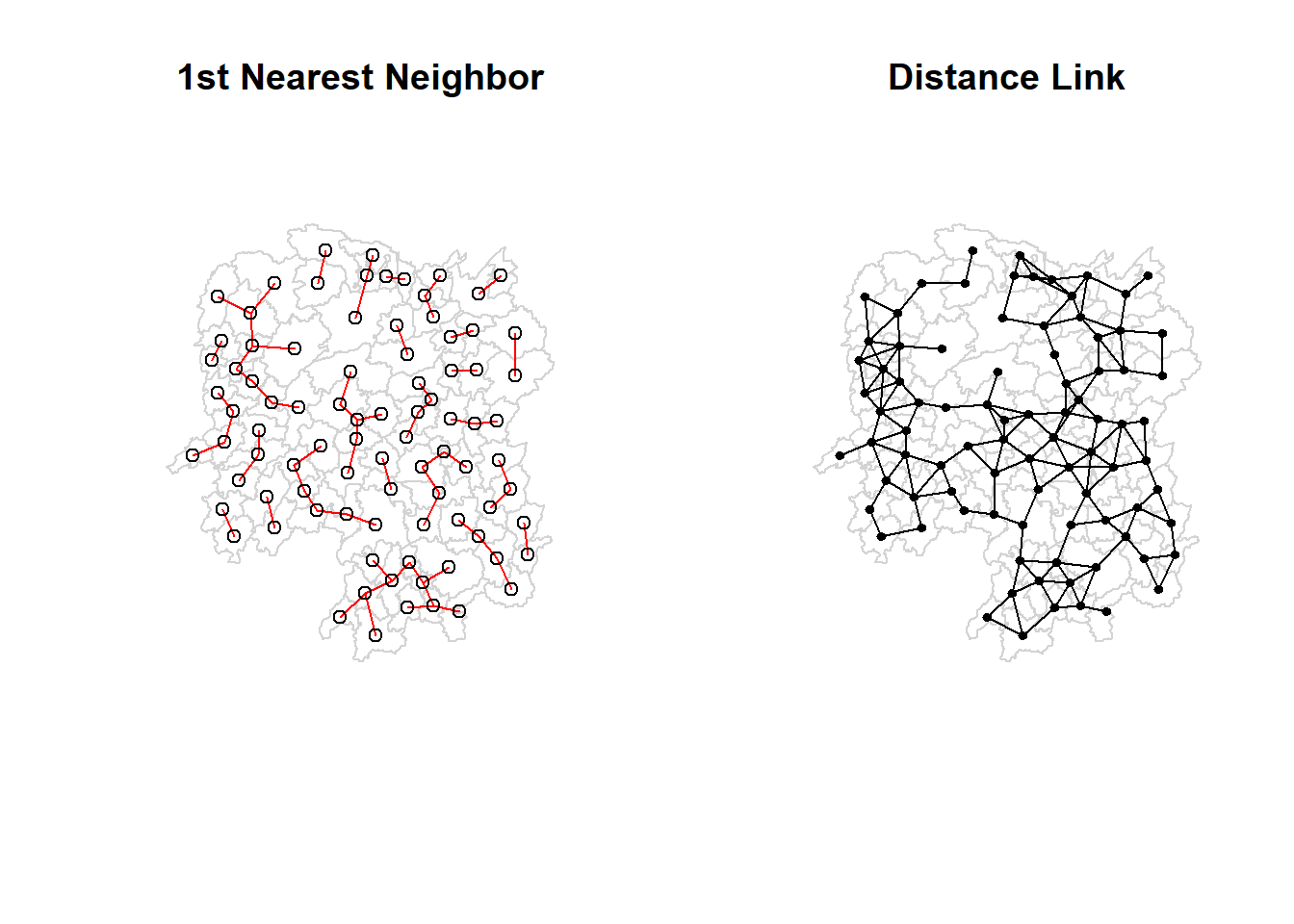
Computing Adaptive Distance Weight Matrix
One of the characteristics of fixed distance weight matrix is that more densely settled areas (usually the urban areas) tend to have more neighbours and the less densely settled areas (usually the rural counties) tend to have fewwer neighbours. Having many neighbours smooths the neighbour relationship across more neighbours.
It is possible to control the numbers of neighbours directly by using k-nearest neighbours, either accepting asymmetric neighbours or imposing symmetry
knn6 <- knn2nb(knearneigh(coords_hunan, k = 6))
knn6Neighbour list object:
Number of regions: 88
Number of nonzero links: 528
Percentage nonzero weights: 6.818182
Average number of links: 6
Non-symmetric neighbours listSimilarly we can display the content of the matrix by using str()
str(knn6)List of 88
$ : int [1:6] 2 3 4 5 57 64
$ : int [1:6] 1 3 57 58 78 85
$ : int [1:6] 1 2 4 5 57 85
$ : int [1:6] 1 3 5 6 69 85
$ : int [1:6] 1 3 4 6 69 85
$ : int [1:6] 3 4 5 69 75 85
$ : int [1:6] 9 66 67 71 74 84
$ : int [1:6] 9 46 47 78 80 86
$ : int [1:6] 8 46 66 68 84 86
$ : int [1:6] 16 19 22 70 72 73
$ : int [1:6] 10 14 16 17 70 72
$ : int [1:6] 13 15 60 61 63 83
$ : int [1:6] 12 15 60 61 63 83
$ : int [1:6] 11 15 16 17 72 83
$ : int [1:6] 12 13 14 17 60 83
$ : int [1:6] 10 11 17 22 72 83
$ : int [1:6] 10 11 14 16 72 83
$ : int [1:6] 20 22 23 63 77 83
$ : int [1:6] 10 20 21 73 74 82
$ : int [1:6] 18 19 21 22 23 82
$ : int [1:6] 19 20 35 74 82 86
$ : int [1:6] 10 16 18 19 20 83
$ : int [1:6] 18 20 41 77 79 82
$ : int [1:6] 25 28 31 52 54 81
$ : int [1:6] 24 28 31 33 54 81
$ : int [1:6] 25 27 29 33 42 81
$ : int [1:6] 26 29 30 37 42 81
$ : int [1:6] 24 25 33 49 52 54
$ : int [1:6] 26 27 37 42 43 81
$ : int [1:6] 26 27 28 33 49 81
$ : int [1:6] 24 25 36 39 40 54
$ : int [1:6] 24 31 50 54 55 56
$ : int [1:6] 25 26 28 30 49 81
$ : int [1:6] 36 40 41 45 56 80
$ : int [1:6] 21 41 46 47 80 82
$ : int [1:6] 31 34 40 45 56 80
$ : int [1:6] 26 27 29 42 43 44
$ : int [1:6] 23 43 44 62 77 79
$ : int [1:6] 25 40 42 43 44 81
$ : int [1:6] 31 36 39 43 45 79
$ : int [1:6] 23 35 45 79 80 82
$ : int [1:6] 26 27 37 39 43 81
$ : int [1:6] 37 39 40 42 44 79
$ : int [1:6] 37 38 39 42 43 79
$ : int [1:6] 34 36 40 41 79 80
$ : int [1:6] 8 9 35 47 78 86
$ : int [1:6] 8 21 35 46 80 86
$ : int [1:6] 49 50 51 52 53 55
$ : int [1:6] 28 33 48 51 52 54
$ : int [1:6] 32 48 51 52 54 55
$ : int [1:6] 28 48 49 50 52 54
$ : int [1:6] 28 48 49 50 51 54
$ : int [1:6] 48 50 51 52 55 75
$ : int [1:6] 24 28 49 50 51 52
$ : int [1:6] 32 48 50 52 53 75
$ : int [1:6] 32 34 36 78 80 85
$ : int [1:6] 1 2 3 58 64 68
$ : int [1:6] 2 57 64 66 68 78
$ : int [1:6] 12 13 60 61 87 88
$ : int [1:6] 12 13 59 61 63 87
$ : int [1:6] 12 13 60 62 63 87
$ : int [1:6] 12 38 61 63 77 87
$ : int [1:6] 12 18 60 61 62 83
$ : int [1:6] 1 3 57 58 68 76
$ : int [1:6] 58 64 66 67 68 76
$ : int [1:6] 9 58 67 68 76 84
$ : int [1:6] 7 65 66 68 76 84
$ : int [1:6] 9 57 58 66 78 84
$ : int [1:6] 4 5 6 32 75 85
$ : int [1:6] 10 16 19 22 72 73
$ : int [1:6] 7 19 73 74 84 86
$ : int [1:6] 10 11 14 16 17 70
$ : int [1:6] 10 19 21 70 71 74
$ : int [1:6] 19 21 71 73 84 86
$ : int [1:6] 6 32 50 53 55 69
$ : int [1:6] 58 64 65 66 67 68
$ : int [1:6] 18 23 38 61 62 63
$ : int [1:6] 2 8 9 46 58 68
$ : int [1:6] 38 40 41 43 44 45
$ : int [1:6] 34 35 36 41 45 47
$ : int [1:6] 25 26 28 33 39 42
$ : int [1:6] 19 20 21 23 35 41
$ : int [1:6] 12 13 15 16 22 63
$ : int [1:6] 7 9 66 68 71 74
$ : int [1:6] 2 3 4 5 56 69
$ : int [1:6] 8 9 21 46 47 74
$ : int [1:6] 59 60 61 62 63 88
$ : int [1:6] 59 60 61 62 63 87
- attr(*, "region.id")= chr [1:88] "1" "2" "3" "4" ...
- attr(*, "call")= language knearneigh(x = coords_hunan, k = 6)
- attr(*, "sym")= logi FALSE
- attr(*, "type")= chr "knn"
- attr(*, "knn-k")= num 6
- attr(*, "class")= chr "nb"Plotting Distance Based Neighbours
We can plot the weight matrix using the code below
plot(hunan$geometry, border = 'lightgrey')
plot(knn6, coords_hunan, pch = 19, cex = 0.6, add = TRUE, col = 'red')
Weight Based on IDW
We can derive a spatial weight matrix based on the Inversed Distance method
nbdists() can be used to compute the distances between areas
dist <- nbdists(wm_q, coords_hunan, longlat = TRUE)
ids <- lapply(dist, function(x) 1/x)
ids[[1]]
[1] 0.01535405 0.03916350 0.01820896 0.02807922 0.01145113
[[2]]
[1] 0.01535405 0.01764308 0.01925924 0.02323898 0.01719350
[[3]]
[1] 0.03916350 0.02822040 0.03695795 0.01395765
[[4]]
[1] 0.01820896 0.02822040 0.03414741 0.01539065
[[5]]
[1] 0.03695795 0.03414741 0.01524598 0.01618354
[[6]]
[1] 0.015390649 0.015245977 0.021748129 0.011883901 0.009810297
[[7]]
[1] 0.01708612 0.01473997 0.01150924 0.01872915
[[8]]
[1] 0.02022144 0.03453056 0.02529256 0.01036340 0.02284457 0.01500600 0.01515314
[[9]]
[1] 0.02022144 0.01574888 0.02109502 0.01508028 0.02902705 0.01502980
[[10]]
[1] 0.02281552 0.01387777 0.01538326 0.01346650 0.02100510 0.02631658 0.01874863
[8] 0.01500046
[[11]]
[1] 0.01882869 0.02243492 0.02247473
[[12]]
[1] 0.02779227 0.02419652 0.02333385 0.02986130 0.02335429
[[13]]
[1] 0.02779227 0.02650020 0.02670323 0.01714243
[[14]]
[1] 0.01882869 0.01233868 0.02098555
[[15]]
[1] 0.02650020 0.01233868 0.01096284 0.01562226
[[16]]
[1] 0.02281552 0.02466962 0.02765018 0.01476814 0.01671430
[[17]]
[1] 0.01387777 0.02243492 0.02098555 0.01096284 0.02466962 0.01593341 0.01437996
[[18]]
[1] 0.02039779 0.02032767 0.01481665 0.01473691 0.01459380
[[19]]
[1] 0.01538326 0.01926323 0.02668415 0.02140253 0.01613589 0.01412874
[[20]]
[1] 0.01346650 0.02039779 0.01926323 0.01723025 0.02153130 0.01469240 0.02327034
[[21]]
[1] 0.02668415 0.01723025 0.01766299 0.02644986 0.02163800
[[22]]
[1] 0.02100510 0.02765018 0.02032767 0.02153130 0.01489296
[[23]]
[1] 0.01481665 0.01469240 0.01401432 0.02246233 0.01880425 0.01530458 0.01849605
[[24]]
[1] 0.02354598 0.01837201 0.02607264 0.01220154 0.02514180
[[25]]
[1] 0.02354598 0.02188032 0.01577283 0.01949232 0.02947957
[[26]]
[1] 0.02155798 0.01745522 0.02212108 0.02220532
[[27]]
[1] 0.02155798 0.02490625 0.01562326
[[28]]
[1] 0.01837201 0.02188032 0.02229549 0.03076171 0.02039506
[[29]]
[1] 0.02490625 0.01686587 0.01395022
[[30]]
[1] 0.02090587
[[31]]
[1] 0.02607264 0.01577283 0.01219005 0.01724850 0.01229012 0.01609781 0.01139438
[8] 0.01150130
[[32]]
[1] 0.01220154 0.01219005 0.01712515 0.01340413 0.01280928 0.01198216 0.01053374
[8] 0.01065655
[[33]]
[1] 0.01949232 0.01745522 0.02229549 0.02090587 0.01979045
[[34]]
[1] 0.03113041 0.03589551 0.02882915
[[35]]
[1] 0.01766299 0.02185795 0.02616766 0.02111721 0.02108253 0.01509020
[[36]]
[1] 0.01724850 0.03113041 0.01571707 0.01860991 0.02073549 0.01680129
[[37]]
[1] 0.01686587 0.02234793 0.01510990 0.01550676
[[38]]
[1] 0.01401432 0.02407426 0.02276151 0.01719415
[[39]]
[1] 0.01229012 0.02172543 0.01711924 0.02629732 0.01896385
[[40]]
[1] 0.01609781 0.01571707 0.02172543 0.01506473 0.01987922 0.01894207
[[41]]
[1] 0.02246233 0.02185795 0.02205991 0.01912542 0.01601083 0.01742892
[[42]]
[1] 0.02212108 0.01562326 0.01395022 0.02234793 0.01711924 0.01836831 0.01683518
[[43]]
[1] 0.01510990 0.02629732 0.01506473 0.01836831 0.03112027 0.01530782
[[44]]
[1] 0.01550676 0.02407426 0.03112027 0.01486508
[[45]]
[1] 0.03589551 0.01860991 0.01987922 0.02205991 0.02107101 0.01982700
[[46]]
[1] 0.03453056 0.04033752 0.02689769
[[47]]
[1] 0.02529256 0.02616766 0.04033752 0.01949145 0.02181458
[[48]]
[1] 0.02313819 0.03370576 0.02289485 0.01630057 0.01818085
[[49]]
[1] 0.03076171 0.02138091 0.02394529 0.01990000
[[50]]
[1] 0.01712515 0.02313819 0.02551427 0.02051530 0.02187179
[[51]]
[1] 0.03370576 0.02138091 0.02873854
[[52]]
[1] 0.02289485 0.02394529 0.02551427 0.02873854 0.03516672
[[53]]
[1] 0.01630057 0.01979945 0.01253977
[[54]]
[1] 0.02514180 0.02039506 0.01340413 0.01990000 0.02051530 0.03516672
[[55]]
[1] 0.01280928 0.01818085 0.02187179 0.01979945 0.01882298
[[56]]
[1] 0.01036340 0.01139438 0.01198216 0.02073549 0.01214479 0.01362855 0.01341697
[[57]]
[1] 0.028079221 0.017643082 0.031423501 0.029114131 0.013520292 0.009903702
[[58]]
[1] 0.01925924 0.03142350 0.02722997 0.01434859 0.01567192
[[59]]
[1] 0.01696711 0.01265572 0.01667105 0.01785036
[[60]]
[1] 0.02419652 0.02670323 0.01696711 0.02343040
[[61]]
[1] 0.02333385 0.01265572 0.02343040 0.02514093 0.02790764 0.01219751 0.02362452
[[62]]
[1] 0.02514093 0.02002219 0.02110260
[[63]]
[1] 0.02986130 0.02790764 0.01407043 0.01805987
[[64]]
[1] 0.02911413 0.01689892
[[65]]
[1] 0.02471705
[[66]]
[1] 0.01574888 0.01726461 0.03068853 0.01954805 0.01810569
[[67]]
[1] 0.01708612 0.01726461 0.01349843 0.01361172
[[68]]
[1] 0.02109502 0.02722997 0.03068853 0.01406357 0.01546511
[[69]]
[1] 0.02174813 0.01645838 0.01419926
[[70]]
[1] 0.02631658 0.01963168 0.02278487
[[71]]
[1] 0.01473997 0.01838483 0.03197403
[[72]]
[1] 0.01874863 0.02247473 0.01476814 0.01593341 0.01963168
[[73]]
[1] 0.01500046 0.02140253 0.02278487 0.01838483 0.01652709
[[74]]
[1] 0.01150924 0.01613589 0.03197403 0.01652709 0.01342099 0.02864567
[[75]]
[1] 0.011883901 0.010533736 0.012539774 0.018822977 0.016458383 0.008217581
[[76]]
[1] 0.01352029 0.01434859 0.01689892 0.02471705 0.01954805 0.01349843 0.01406357
[[77]]
[1] 0.014736909 0.018804247 0.022761507 0.012197506 0.020022195 0.014070428
[7] 0.008440896
[[78]]
[1] 0.02323898 0.02284457 0.01508028 0.01214479 0.01567192 0.01546511 0.01140779
[[79]]
[1] 0.01530458 0.01719415 0.01894207 0.01912542 0.01530782 0.01486508 0.02107101
[[80]]
[1] 0.01500600 0.02882915 0.02111721 0.01680129 0.01601083 0.01982700 0.01949145
[8] 0.01362855
[[81]]
[1] 0.02947957 0.02220532 0.01150130 0.01979045 0.01896385 0.01683518
[[82]]
[1] 0.02327034 0.02644986 0.01849605 0.02108253 0.01742892
[[83]]
[1] 0.023354289 0.017142433 0.015622258 0.016714303 0.014379961 0.014593799
[7] 0.014892965 0.018059871 0.008440896
[[84]]
[1] 0.01872915 0.02902705 0.01810569 0.01361172 0.01342099 0.01297994
[[85]]
[1] 0.011451133 0.017193502 0.013957649 0.016183544 0.009810297 0.010656545
[7] 0.013416965 0.009903702 0.014199260 0.008217581 0.011407794
[[86]]
[1] 0.01515314 0.01502980 0.01412874 0.02163800 0.01509020 0.02689769 0.02181458
[8] 0.02864567 0.01297994
[[87]]
[1] 0.01667105 0.02362452 0.02110260 0.02058034
[[88]]
[1] 0.01785036 0.02058034Row-standardised Weights Matrix
Next, we assign weights to each neighboring polygon.
Each neighboring polygon will be assigned equal weight (style = “W”). This is accomplished by assigning the fraction of 1/(#ofneighbors) to each neighboring county then summing the weighted income values. While this is the most intuitive way to summarise the neighbors’ values, it has one drawback in that polygons along the edges of the study area will base their lagged values on fewer polygons thus potentially over- or under-estimating the true nature of the spatial autocorrelation in the data.
For this example, we’ll stick with the style=“W” option for simplicity’s sake but note that other more robust options are available, notably style=“B”.
rswm_q <- nb2listw(wm_q, style='W', zero.policy = TRUE)
rswm_qCharacteristics of weights list object:
Neighbour list object:
Number of regions: 88
Number of nonzero links: 448
Percentage nonzero weights: 5.785124
Average number of links: 5.090909
Weights style: W
Weights constants summary:
n nn S0 S1 S2
W 88 7744 88 37.86334 365.9147The zero.policy = TRUE option allows for lists of non-neighbors. This should be used with caution since the user may not be aware of missing neighbors in their dataset. However, a zero.policy of FALSE would return an error.
To see the weight of the first polygon’s eight neighbors:
rswm_q$weights[10][[1]]
[1] 0.125 0.125 0.125 0.125 0.125 0.125 0.125 0.125Each neighbor is assigned a 0.125 of the total weight. This means that when R computes the average neighboring income values, each neighbor’s income will be multiplied by 0.2 before being tallied.
We can use the same method to derive a row standardised distance weight matrix.
rswm_ids <- nb2listw(wm_q, glist = ids, style = 'B', zero.policy = TRUE)
rswm_idsCharacteristics of weights list object:
Neighbour list object:
Number of regions: 88
Number of nonzero links: 448
Percentage nonzero weights: 5.785124
Average number of links: 5.090909
Weights style: B
Weights constants summary:
n nn S0 S1 S2
B 88 7744 8.786867 0.3776535 3.8137To see the weight of the first polygon’s neighbours
rswm_ids$weights[1][[1]]
[1] 0.01535405 0.03916350 0.01820896 0.02807922 0.01145113We can see the summary of the weights by using summary()
summary(unlist(rswm_ids$weights)) Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
0.008218 0.015088 0.018739 0.019614 0.022823 0.040338 Application of Spatial Weight Matrix
In this section we will create four different spatial lagged variables:
spatial lag with row-standardized weights
spatial lag as a sum of neighbouring values
spatial window average
spatial window sum
Spatial Lag with Row-standardized Weights
We will compute the average neighbor GDPPC value for each polygon
GDPPC.lag <- lag.listw(rswm_q, hunan$GDPPC)
GDPPC.lag [1] 24847.20 22724.80 24143.25 27737.50 27270.25 21248.80 43747.00 33582.71
[9] 45651.17 32027.62 32671.00 20810.00 25711.50 30672.33 33457.75 31689.20
[17] 20269.00 23901.60 25126.17 21903.43 22718.60 25918.80 20307.00 20023.80
[25] 16576.80 18667.00 14394.67 19848.80 15516.33 20518.00 17572.00 15200.12
[33] 18413.80 14419.33 24094.50 22019.83 12923.50 14756.00 13869.80 12296.67
[41] 15775.17 14382.86 11566.33 13199.50 23412.00 39541.00 36186.60 16559.60
[49] 20772.50 19471.20 19827.33 15466.80 12925.67 18577.17 14943.00 24913.00
[57] 25093.00 24428.80 17003.00 21143.75 20435.00 17131.33 24569.75 23835.50
[65] 26360.00 47383.40 55157.75 37058.00 21546.67 23348.67 42323.67 28938.60
[73] 25880.80 47345.67 18711.33 29087.29 20748.29 35933.71 15439.71 29787.50
[81] 18145.00 21617.00 29203.89 41363.67 22259.09 44939.56 16902.00 16930.00Recalled in the previous section, we retrieved the GDPPC of these five counties
nb1 <- wm_q[[1]]
nb1_gdppc <- hunan$GDPPC[nb1]
nb1_gdppc[1] 20981 34592 24473 21311 22879Question: Can you see the meaning of Spatial lag with row-standardized weights?
For better comparison, we can try to print both series of values
print(GDPPC.lag[wm_q[[1]]])[1] 22724.80 24143.25 27737.50 25093.00 22259.09print(nb1_gdppc)[1] 20981 34592 24473 21311 22879Possible Answer: Most neighbors were adjusted slightly based on their weights, particularly neighbor id 3. This accounts geographical distance into the GDPPC value of each neighbor, accounting for the influence on the value of GDPPC by the values of GDPPC of its neighbours.
We can append the spatially lag GDPPC values onto hunan sf data frame by using the code chunk below.
lag.list <- list(hunan$NAME_3, lag.listw(rswm_q, hunan$GDPPC))
lag.res <- as.data.frame(lag.list)
colnames(lag.res) <- c('NAME_3', 'lag GDPPC')
hunan <- left_join(hunan,lag.res)We can see the new spatial lag GDPPC using head()
head(hunan)Simple feature collection with 6 features and 7 fields
Geometry type: POLYGON
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 110.4922 ymin: 28.61762 xmax: 112.3013 ymax: 30.12812
Geodetic CRS: WGS 84
NAME_2 ID_3 NAME_3 ENGTYPE_3 County GDPPC lag GDPPC
1 Changde 21098 Anxiang County Anxiang 23667 24847.20
2 Changde 21100 Hanshou County Hanshou 20981 22724.80
3 Changde 21101 Jinshi County City Jinshi 34592 24143.25
4 Changde 21102 Li County Li 24473 27737.50
5 Changde 21103 Linli County Linli 25554 27270.25
6 Changde 21104 Shimen County Shimen 27137 21248.80
geometry
1 POLYGON ((112.0625 29.75523...
2 POLYGON ((112.2288 29.11684...
3 POLYGON ((111.8927 29.6013,...
4 POLYGON ((111.3731 29.94649...
5 POLYGON ((111.6324 29.76288...
6 POLYGON ((110.8825 30.11675...Next, we can plot the GDPPC and spatial lag GDPPC for comparison
gdppc <- qtm(hunan, "GDPPC")
lag_gdppc <- qtm(hunan, "lag GDPPC")
tmap_arrange(gdppc, lag_gdppc, asp = 1, ncol = 2)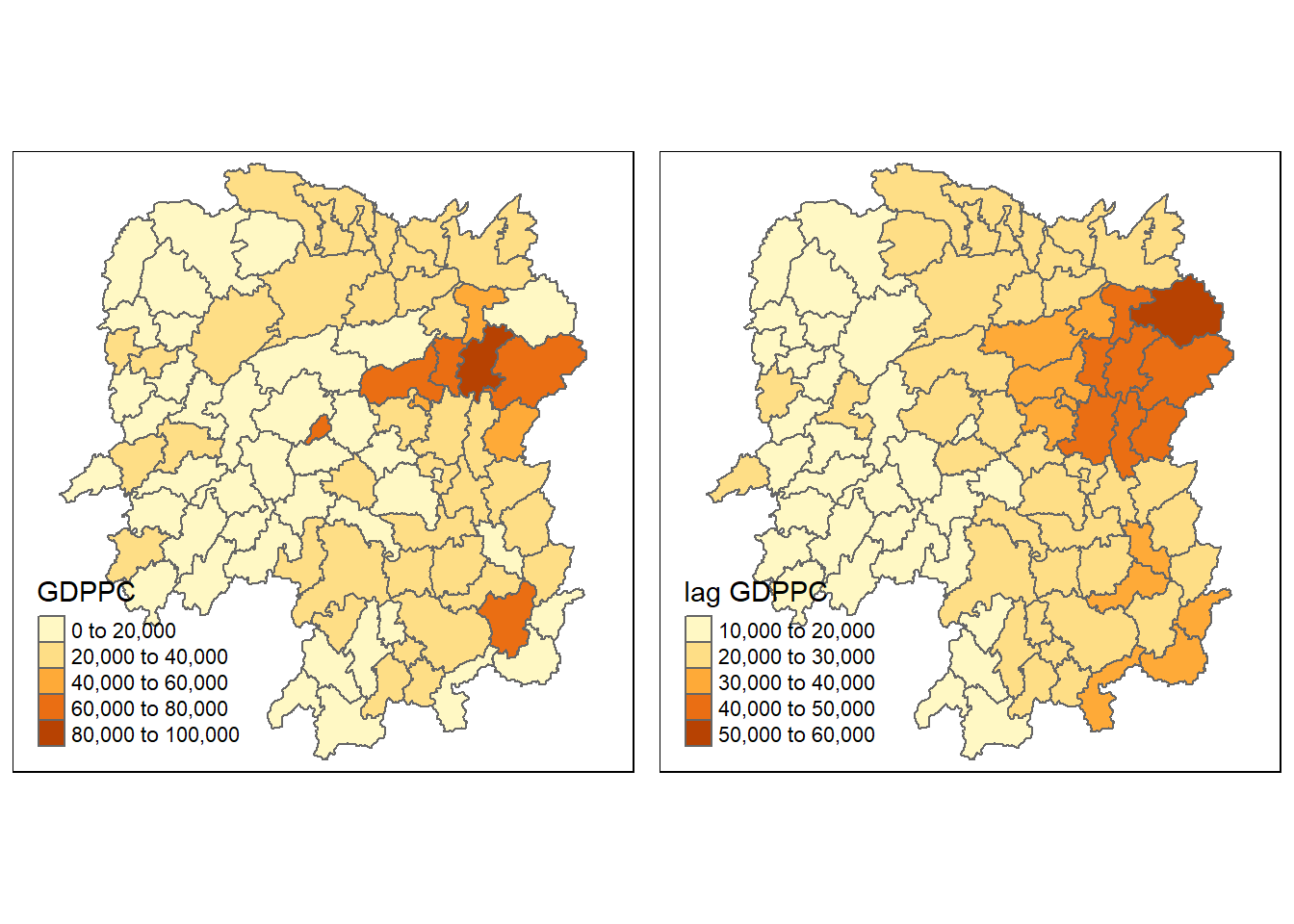
Spatial Lag as a Sum of Neighboring Values
We can calculate spatial lag a sum of neighboring values by assigning binary weights. This requires us to go back to our neighbors list, then apply a function that will assign binary weights, then we use glist= in the nb2listw function to explicitly assign these weights.
We start by applying a function that will assign a value of 1 per each neighbor. This is done with lapply, which we have been using to manipulate the neighbors structure throughout the past notebooks. Basically it applies a function across each value in the neighbor structure.
b_weights <- lapply(wm_q, function(x) 0*x + 1)
b_weights2 <- nb2listw(wm_q,
glist = b_weights,
style = 'B')
b_weights2Characteristics of weights list object:
Neighbour list object:
Number of regions: 88
Number of nonzero links: 448
Percentage nonzero weights: 5.785124
Average number of links: 5.090909
Weights style: B
Weights constants summary:
n nn S0 S1 S2
B 88 7744 448 896 10224With proper weights assigned, we can use lag.listw to compute a lag variable from our weight and GDPPC
lag_sum <- list(hunan$NAME_3, lag.listw(b_weights2, hunan$GDPPC))
lag.res <- as.data.frame(lag_sum)
colnames(lag.res) <- c('NAME_3', 'lag_sum GDPPC')We can take a glimpse of the newly created data frame
lag.res NAME_3 lag_sum GDPPC
1 Anxiang 124236
2 Hanshou 113624
3 Jinshi 96573
4 Li 110950
5 Linli 109081
6 Shimen 106244
7 Liuyang 174988
8 Ningxiang 235079
9 Wangcheng 273907
10 Anren 256221
11 Guidong 98013
12 Jiahe 104050
13 Linwu 102846
14 Rucheng 92017
15 Yizhang 133831
16 Yongxing 158446
17 Zixing 141883
18 Changning 119508
19 Hengdong 150757
20 Hengnan 153324
21 Hengshan 113593
22 Leiyang 129594
23 Qidong 142149
24 Chenxi 100119
25 Zhongfang 82884
26 Huitong 74668
27 Jingzhou 43184
28 Mayang 99244
29 Tongdao 46549
30 Xinhuang 20518
31 Xupu 140576
32 Yuanling 121601
33 Zhijiang 92069
34 Lengshuijiang 43258
35 Shuangfeng 144567
36 Xinhua 132119
37 Chengbu 51694
38 Dongan 59024
39 Dongkou 69349
40 Longhui 73780
41 Shaodong 94651
42 Suining 100680
43 Wugang 69398
44 Xinning 52798
45 Xinshao 140472
46 Shaoshan 118623
47 Xiangxiang 180933
48 Baojing 82798
49 Fenghuang 83090
50 Guzhang 97356
51 Huayuan 59482
52 Jishou 77334
53 Longshan 38777
54 Luxi 111463
55 Yongshun 74715
56 Anhua 174391
57 Nan 150558
58 Yuanjiang 122144
59 Jianghua 68012
60 Lanshan 84575
61 Ningyuan 143045
62 Shuangpai 51394
63 Xintian 98279
64 Huarong 47671
65 Linxiang 26360
66 Miluo 236917
67 Pingjiang 220631
68 Xiangyin 185290
69 Cili 64640
70 Chaling 70046
71 Liling 126971
72 Yanling 144693
73 You 129404
74 Zhuzhou 284074
75 Sangzhi 112268
76 Yueyang 203611
77 Qiyang 145238
78 Taojiang 251536
79 Shaoyang 108078
80 Lianyuan 238300
81 Hongjiang 108870
82 Hengyang 108085
83 Guiyang 262835
84 Changsha 248182
85 Taoyuan 244850
86 Xiangtan 404456
87 Dao 67608
88 Jiangyong 33860Question: Can you understand the meaning of Spatial Lag as a Sum of Neighboring Values?
Answer: Instead of using the GDPPC value of the polygon, this method sums the GDPPC values of all of its neighbors
We can append the lag_sum GDPPC field into the hunan sf data frame
hunan <- left_join(hunan, lag.res)Next, we can plot the GDPPC and spatial lag as sum of neighbors GDPPC for comparison
gdppc <- qtm(hunan, 'GDPPC')
lag_sum_gdppc <- qtm(hunan, 'lag_sum GDPPC')
tmap_arrange(gdppc, lag_sum_gdppc, asp = 1, ncol = 2)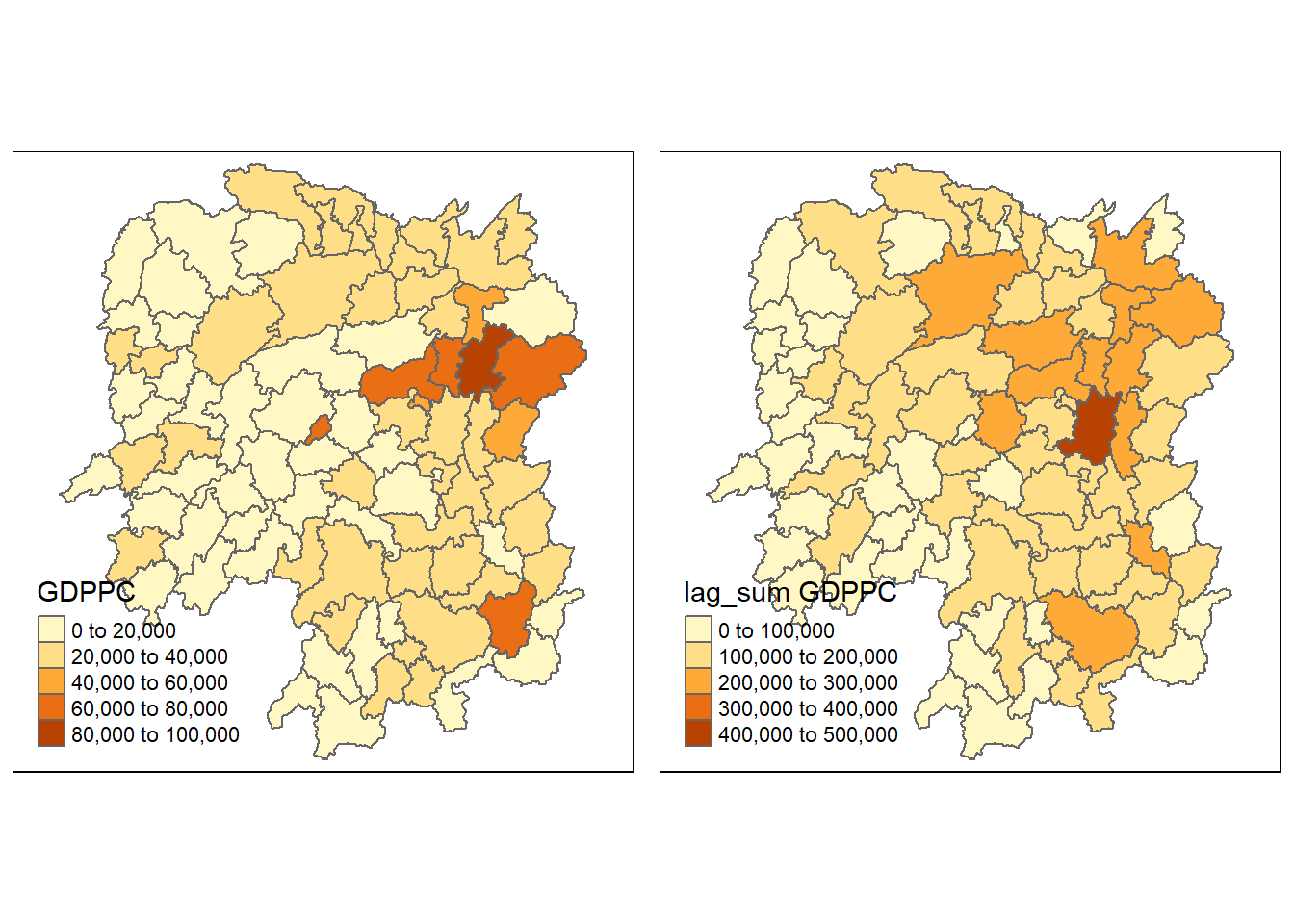
Spatial Window Average
The spatial window average uses row-standardized weights and includes the diagonal element, or the self-weight. To do this in R, we need to go back to the neighbors structure and add the diagonal element before assigning weights.
To add the diagonal element to the neighbour list, we need to use include.self() from spdep.
wm_qs <- include.self(wm_q)Notice that the Number of nonzero links, Percentage nonzero weights and Average number of links are 536, 6.921488 and 6.090909 respectively as compared to wm_q of 448, 5.785124 and 5.090909
We can take a good look at the neighbour list of area [1]
wm_qs[[1]][1] 1 2 3 4 57 85Now, [1] has six neighbours instead of five, including itself.
Now we can obtain the weights with nb2listw()
wm_qs <- nb2listw(wm_qs)
wm_qsCharacteristics of weights list object:
Neighbour list object:
Number of regions: 88
Number of nonzero links: 536
Percentage nonzero weights: 6.921488
Average number of links: 6.090909
Weights style: W
Weights constants summary:
n nn S0 S1 S2
W 88 7744 88 30.90265 357.5308Lastly, we can create the lag variable from our weight structure and GDPPC variable
lag_w_avg_gdppc <- lag.listw(wm_qs, hunan$GDPPC)
lag_w_avg_gdppc [1] 24650.50 22434.17 26233.00 27084.60 26927.00 22230.17 47621.20 37160.12
[9] 49224.71 29886.89 26627.50 22690.17 25366.40 25825.75 30329.00 32682.83
[17] 25948.62 23987.67 25463.14 21904.38 23127.50 25949.83 20018.75 19524.17
[25] 18955.00 17800.40 15883.00 18831.33 14832.50 17965.00 17159.89 16199.44
[33] 18764.50 26878.75 23188.86 20788.14 12365.20 15985.00 13764.83 11907.43
[41] 17128.14 14593.62 11644.29 12706.00 21712.29 43548.25 35049.00 16226.83
[49] 19294.40 18156.00 19954.75 18145.17 12132.75 18419.29 14050.83 23619.75
[57] 24552.71 24733.67 16762.60 20932.60 19467.75 18334.00 22541.00 26028.00
[65] 29128.50 46569.00 47576.60 36545.50 20838.50 22531.00 42115.50 27619.00
[73] 27611.33 44523.29 18127.43 28746.38 20734.50 33880.62 14716.38 28516.22
[81] 18086.14 21244.50 29568.80 48119.71 22310.75 43151.60 17133.40 17009.33Next, we will convert the lag variable listw into a data frame similar to what we have done previously
lag.list.wm_qs <- list(hunan$NAME_3, lag.listw(wm_qs, hunan$GDPPC))
lag_wm_qs.res <- as.data.frame(lag.list.wm_qs)
colnames(lag_wm_qs.res) <- c('NAME_3', 'lag_window_avg GDPPC')Now, we can append this data frame onto the original hunan sf data frame
hunan <- left_join(hunan, lag_wm_qs.res)To compare the values of lag GDPPC and Spatial Window Average, kable() is used
hunan %>%
select('County', 'lag GDPPC', 'lag_window_avg GDPPC') %>%
kable()| County | lag GDPPC | lag_window_avg GDPPC | geometry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anxiang | 24847.20 | 24650.50 | POLYGON ((112.0625 29.75523… |
| Hanshou | 22724.80 | 22434.17 | POLYGON ((112.2288 29.11684… |
| Jinshi | 24143.25 | 26233.00 | POLYGON ((111.8927 29.6013,… |
| Li | 27737.50 | 27084.60 | POLYGON ((111.3731 29.94649… |
| Linli | 27270.25 | 26927.00 | POLYGON ((111.6324 29.76288… |
| Shimen | 21248.80 | 22230.17 | POLYGON ((110.8825 30.11675… |
| Liuyang | 43747.00 | 47621.20 | POLYGON ((113.9905 28.5682,… |
| Ningxiang | 33582.71 | 37160.12 | POLYGON ((112.7181 28.38299… |
| Wangcheng | 45651.17 | 49224.71 | POLYGON ((112.7914 28.52688… |
| Anren | 32027.62 | 29886.89 | POLYGON ((113.1757 26.82734… |
| Guidong | 32671.00 | 26627.50 | POLYGON ((114.1799 26.20117… |
| Jiahe | 20810.00 | 22690.17 | POLYGON ((112.4425 25.74358… |
| Linwu | 25711.50 | 25366.40 | POLYGON ((112.5914 25.55143… |
| Rucheng | 30672.33 | 25825.75 | POLYGON ((113.6759 25.87578… |
| Yizhang | 33457.75 | 30329.00 | POLYGON ((113.2621 25.68394… |
| Yongxing | 31689.20 | 32682.83 | POLYGON ((113.3169 26.41843… |
| Zixing | 20269.00 | 25948.62 | POLYGON ((113.7311 26.16259… |
| Changning | 23901.60 | 23987.67 | POLYGON ((112.6144 26.60198… |
| Hengdong | 25126.17 | 25463.14 | POLYGON ((113.1056 27.21007… |
| Hengnan | 21903.43 | 21904.38 | POLYGON ((112.7599 26.98149… |
| Hengshan | 22718.60 | 23127.50 | POLYGON ((112.607 27.4689, … |
| Leiyang | 25918.80 | 25949.83 | POLYGON ((112.9996 26.69276… |
| Qidong | 20307.00 | 20018.75 | POLYGON ((111.7818 27.0383,… |
| Chenxi | 20023.80 | 19524.17 | POLYGON ((110.2624 28.21778… |
| Zhongfang | 16576.80 | 18955.00 | POLYGON ((109.9431 27.72858… |
| Huitong | 18667.00 | 17800.40 | POLYGON ((109.9419 27.10512… |
| Jingzhou | 14394.67 | 15883.00 | POLYGON ((109.8186 26.75842… |
| Mayang | 19848.80 | 18831.33 | POLYGON ((109.795 27.98008,… |
| Tongdao | 15516.33 | 14832.50 | POLYGON ((109.9294 26.46561… |
| Xinhuang | 20518.00 | 17965.00 | POLYGON ((109.227 27.43733,… |
| Xupu | 17572.00 | 17159.89 | POLYGON ((110.7189 28.30485… |
| Yuanling | 15200.12 | 16199.44 | POLYGON ((110.9652 28.99895… |
| Zhijiang | 18413.80 | 18764.50 | POLYGON ((109.8818 27.60661… |
| Lengshuijiang | 14419.33 | 26878.75 | POLYGON ((111.5307 27.81472… |
| Shuangfeng | 24094.50 | 23188.86 | POLYGON ((112.263 27.70421,… |
| Xinhua | 22019.83 | 20788.14 | POLYGON ((111.3345 28.19642… |
| Chengbu | 12923.50 | 12365.20 | POLYGON ((110.4455 26.69317… |
| Dongan | 14756.00 | 15985.00 | POLYGON ((111.4531 26.86812… |
| Dongkou | 13869.80 | 13764.83 | POLYGON ((110.6622 27.37305… |
| Longhui | 12296.67 | 11907.43 | POLYGON ((110.985 27.65983,… |
| Shaodong | 15775.17 | 17128.14 | POLYGON ((111.9054 27.40254… |
| Suining | 14382.86 | 14593.62 | POLYGON ((110.389 27.10006,… |
| Wugang | 11566.33 | 11644.29 | POLYGON ((110.9878 27.03345… |
| Xinning | 13199.50 | 12706.00 | POLYGON ((111.0736 26.84627… |
| Xinshao | 23412.00 | 21712.29 | POLYGON ((111.6013 27.58275… |
| Shaoshan | 39541.00 | 43548.25 | POLYGON ((112.5391 27.97742… |
| Xiangxiang | 36186.60 | 35049.00 | POLYGON ((112.4549 28.05783… |
| Baojing | 16559.60 | 16226.83 | POLYGON ((109.7015 28.82844… |
| Fenghuang | 20772.50 | 19294.40 | POLYGON ((109.5239 28.19206… |
| Guzhang | 19471.20 | 18156.00 | POLYGON ((109.8968 28.74034… |
| Huayuan | 19827.33 | 19954.75 | POLYGON ((109.5647 28.61712… |
| Jishou | 15466.80 | 18145.17 | POLYGON ((109.8375 28.4696,… |
| Longshan | 12925.67 | 12132.75 | POLYGON ((109.6337 29.62521… |
| Luxi | 18577.17 | 18419.29 | POLYGON ((110.1067 28.41835… |
| Yongshun | 14943.00 | 14050.83 | POLYGON ((110.0003 29.29499… |
| Anhua | 24913.00 | 23619.75 | POLYGON ((111.6034 28.63716… |
| Nan | 25093.00 | 24552.71 | POLYGON ((112.3232 29.46074… |
| Yuanjiang | 24428.80 | 24733.67 | POLYGON ((112.4391 29.1791,… |
| Jianghua | 17003.00 | 16762.60 | POLYGON ((111.6461 25.29661… |
| Lanshan | 21143.75 | 20932.60 | POLYGON ((112.2286 25.61123… |
| Ningyuan | 20435.00 | 19467.75 | POLYGON ((112.0715 26.09892… |
| Shuangpai | 17131.33 | 18334.00 | POLYGON ((111.8864 26.11957… |
| Xintian | 24569.75 | 22541.00 | POLYGON ((112.2578 26.0796,… |
| Huarong | 23835.50 | 26028.00 | POLYGON ((112.9242 29.69134… |
| Linxiang | 26360.00 | 29128.50 | POLYGON ((113.5502 29.67418… |
| Miluo | 47383.40 | 46569.00 | POLYGON ((112.9902 29.02139… |
| Pingjiang | 55157.75 | 47576.60 | POLYGON ((113.8436 29.06152… |
| Xiangyin | 37058.00 | 36545.50 | POLYGON ((112.9173 28.98264… |
| Cili | 21546.67 | 20838.50 | POLYGON ((110.8822 29.69017… |
| Chaling | 23348.67 | 22531.00 | POLYGON ((113.7666 27.10573… |
| Liling | 42323.67 | 42115.50 | POLYGON ((113.5673 27.94346… |
| Yanling | 28938.60 | 27619.00 | POLYGON ((113.9292 26.6154,… |
| You | 25880.80 | 27611.33 | POLYGON ((113.5879 27.41324… |
| Zhuzhou | 47345.67 | 44523.29 | POLYGON ((113.2493 28.02411… |
| Sangzhi | 18711.33 | 18127.43 | POLYGON ((110.556 29.40543,… |
| Yueyang | 29087.29 | 28746.38 | POLYGON ((113.343 29.61064,… |
| Qiyang | 20748.29 | 20734.50 | POLYGON ((111.5563 26.81318… |
| Taojiang | 35933.71 | 33880.62 | POLYGON ((112.0508 28.67265… |
| Shaoyang | 15439.71 | 14716.38 | POLYGON ((111.5013 27.30207… |
| Lianyuan | 29787.50 | 28516.22 | POLYGON ((111.6789 28.02946… |
| Hongjiang | 18145.00 | 18086.14 | POLYGON ((110.1441 27.47513… |
| Hengyang | 21617.00 | 21244.50 | POLYGON ((112.7144 26.98613… |
| Guiyang | 29203.89 | 29568.80 | POLYGON ((113.0811 26.04963… |
| Changsha | 41363.67 | 48119.71 | POLYGON ((112.9421 28.03722… |
| Taoyuan | 22259.09 | 22310.75 | POLYGON ((112.0612 29.32855… |
| Xiangtan | 44939.56 | 43151.60 | POLYGON ((113.0426 27.8942,… |
| Dao | 16902.00 | 17133.40 | POLYGON ((111.498 25.81679,… |
| Jiangyong | 16930.00 | 17009.33 | POLYGON ((111.3659 25.39472… |
Finally, we can create two plots in order to compare how lag GDPPC and lag_window_avg GDPPC are plotted
w_avg_gdppc <- qtm(hunan, 'lag_window_avg GDPPC')
tmap_arrange(lag_gdppc, w_avg_gdppc, asp = 1, ncol = 2)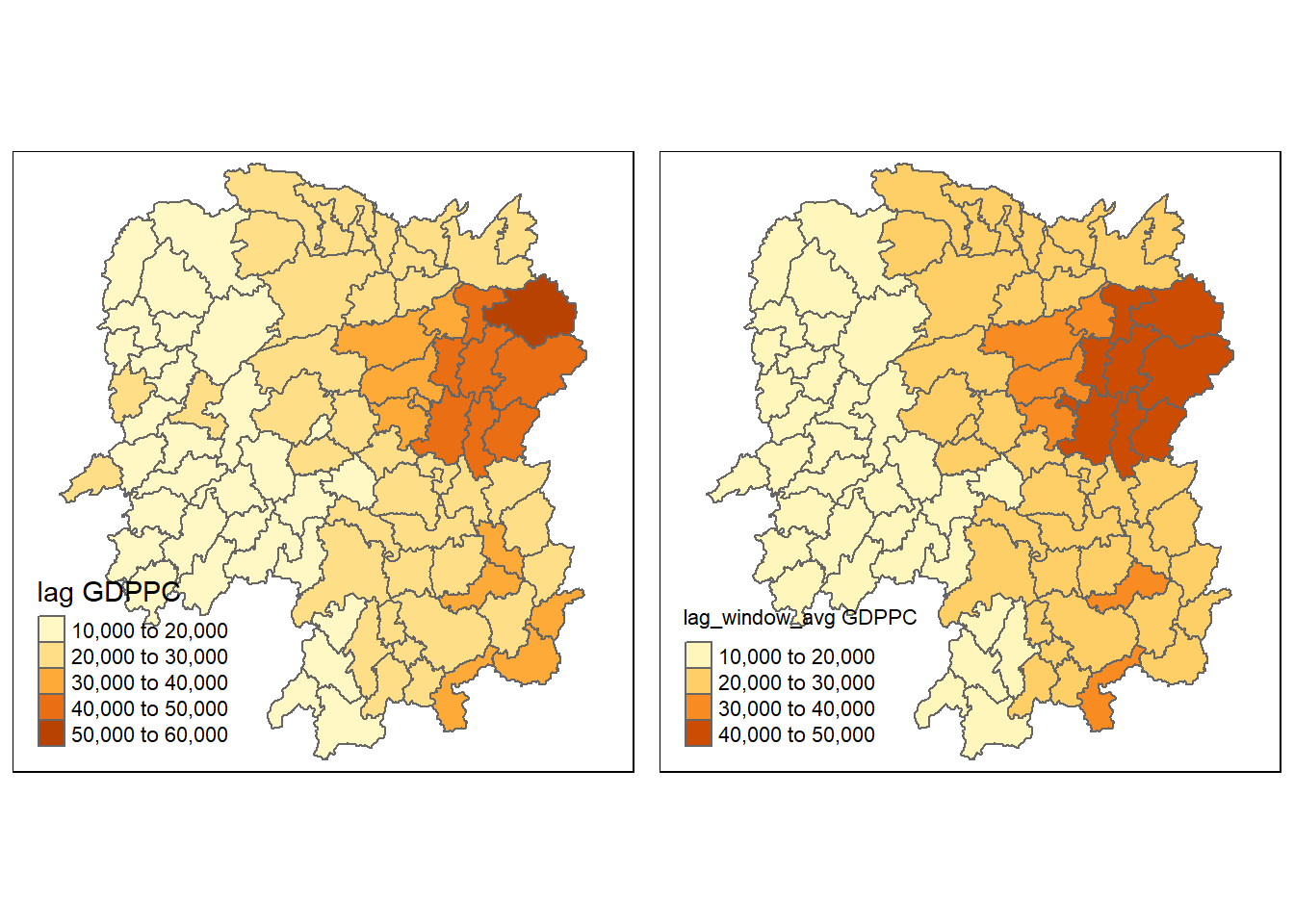
Spatial Window Sum
The spatial window sum is the counterpart of the window average, but without using row-standardized weights.
First, we create the neighbor list including self
wm_qs <- include.self(wm_q)
wm_qsNeighbour list object:
Number of regions: 88
Number of nonzero links: 536
Percentage nonzero weights: 6.921488
Average number of links: 6.090909 Next, we can assign binary weights to the neighbour structure that includes the diagonal element similar to what was done in Spatial Lag as a Sum of Neighboring Values.
b_weights <- lapply(wm_qs, function(x) 0*x+1)
b_weights[1][[1]]
[1] 1 1 1 1 1 1Similar to Spatial Window Average, [1] now has six neighbours
Now we can use nb2listw() to assign weight values, which is now binary
b_weights2 <- nb2listw(wm_qs,
glist = b_weights,
style = 'B')
b_weights2Characteristics of weights list object:
Neighbour list object:
Number of regions: 88
Number of nonzero links: 536
Percentage nonzero weights: 6.921488
Average number of links: 6.090909
Weights style: B
Weights constants summary:
n nn S0 S1 S2
B 88 7744 536 1072 14160With our new weight structure, we can compute the lag variable with lag.listw
w_sum_gdppc <- list(hunan$NAME_3, lag.listw(b_weights2, hunan$GDPPC))
w_sum_gdppc[[1]]
[1] "Anxiang" "Hanshou" "Jinshi" "Li"
[5] "Linli" "Shimen" "Liuyang" "Ningxiang"
[9] "Wangcheng" "Anren" "Guidong" "Jiahe"
[13] "Linwu" "Rucheng" "Yizhang" "Yongxing"
[17] "Zixing" "Changning" "Hengdong" "Hengnan"
[21] "Hengshan" "Leiyang" "Qidong" "Chenxi"
[25] "Zhongfang" "Huitong" "Jingzhou" "Mayang"
[29] "Tongdao" "Xinhuang" "Xupu" "Yuanling"
[33] "Zhijiang" "Lengshuijiang" "Shuangfeng" "Xinhua"
[37] "Chengbu" "Dongan" "Dongkou" "Longhui"
[41] "Shaodong" "Suining" "Wugang" "Xinning"
[45] "Xinshao" "Shaoshan" "Xiangxiang" "Baojing"
[49] "Fenghuang" "Guzhang" "Huayuan" "Jishou"
[53] "Longshan" "Luxi" "Yongshun" "Anhua"
[57] "Nan" "Yuanjiang" "Jianghua" "Lanshan"
[61] "Ningyuan" "Shuangpai" "Xintian" "Huarong"
[65] "Linxiang" "Miluo" "Pingjiang" "Xiangyin"
[69] "Cili" "Chaling" "Liling" "Yanling"
[73] "You" "Zhuzhou" "Sangzhi" "Yueyang"
[77] "Qiyang" "Taojiang" "Shaoyang" "Lianyuan"
[81] "Hongjiang" "Hengyang" "Guiyang" "Changsha"
[85] "Taoyuan" "Xiangtan" "Dao" "Jiangyong"
[[2]]
[1] 147903 134605 131165 135423 134635 133381 238106 297281 344573 268982
[11] 106510 136141 126832 103303 151645 196097 207589 143926 178242 175235
[21] 138765 155699 160150 117145 113730 89002 63532 112988 59330 35930
[31] 154439 145795 112587 107515 162322 145517 61826 79925 82589 83352
[41] 119897 116749 81510 63530 151986 174193 210294 97361 96472 108936
[51] 79819 108871 48531 128935 84305 188958 171869 148402 83813 104663
[61] 155742 73336 112705 78084 58257 279414 237883 219273 83354 90124
[71] 168462 165714 165668 311663 126892 229971 165876 271045 117731 256646
[81] 126603 127467 295688 336838 267729 431516 85667 51028Next, we will convert this object into a data frame
w_sum_gdppc.res <- as.data.frame(w_sum_gdppc)
colnames(w_sum_gdppc.res) <- c('NAME_3', 'w_sum GDPPC')Next, we will join it with the original hunan data frame
hunan <- left_join(hunan, w_sum_gdppc.res)To compare the values of lag GDPPC and Spatial window average, kable() of Knitr package is used to prepare a table using the code chunk below.
hunan %>%
select('County', 'lag_sum GDPPC', 'w_sum GDPPC') %>%
kable()| County | lag_sum GDPPC | w_sum GDPPC | geometry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anxiang | 124236 | 147903 | POLYGON ((112.0625 29.75523… |
| Hanshou | 113624 | 134605 | POLYGON ((112.2288 29.11684… |
| Jinshi | 96573 | 131165 | POLYGON ((111.8927 29.6013,… |
| Li | 110950 | 135423 | POLYGON ((111.3731 29.94649… |
| Linli | 109081 | 134635 | POLYGON ((111.6324 29.76288… |
| Shimen | 106244 | 133381 | POLYGON ((110.8825 30.11675… |
| Liuyang | 174988 | 238106 | POLYGON ((113.9905 28.5682,… |
| Ningxiang | 235079 | 297281 | POLYGON ((112.7181 28.38299… |
| Wangcheng | 273907 | 344573 | POLYGON ((112.7914 28.52688… |
| Anren | 256221 | 268982 | POLYGON ((113.1757 26.82734… |
| Guidong | 98013 | 106510 | POLYGON ((114.1799 26.20117… |
| Jiahe | 104050 | 136141 | POLYGON ((112.4425 25.74358… |
| Linwu | 102846 | 126832 | POLYGON ((112.5914 25.55143… |
| Rucheng | 92017 | 103303 | POLYGON ((113.6759 25.87578… |
| Yizhang | 133831 | 151645 | POLYGON ((113.2621 25.68394… |
| Yongxing | 158446 | 196097 | POLYGON ((113.3169 26.41843… |
| Zixing | 141883 | 207589 | POLYGON ((113.7311 26.16259… |
| Changning | 119508 | 143926 | POLYGON ((112.6144 26.60198… |
| Hengdong | 150757 | 178242 | POLYGON ((113.1056 27.21007… |
| Hengnan | 153324 | 175235 | POLYGON ((112.7599 26.98149… |
| Hengshan | 113593 | 138765 | POLYGON ((112.607 27.4689, … |
| Leiyang | 129594 | 155699 | POLYGON ((112.9996 26.69276… |
| Qidong | 142149 | 160150 | POLYGON ((111.7818 27.0383,… |
| Chenxi | 100119 | 117145 | POLYGON ((110.2624 28.21778… |
| Zhongfang | 82884 | 113730 | POLYGON ((109.9431 27.72858… |
| Huitong | 74668 | 89002 | POLYGON ((109.9419 27.10512… |
| Jingzhou | 43184 | 63532 | POLYGON ((109.8186 26.75842… |
| Mayang | 99244 | 112988 | POLYGON ((109.795 27.98008,… |
| Tongdao | 46549 | 59330 | POLYGON ((109.9294 26.46561… |
| Xinhuang | 20518 | 35930 | POLYGON ((109.227 27.43733,… |
| Xupu | 140576 | 154439 | POLYGON ((110.7189 28.30485… |
| Yuanling | 121601 | 145795 | POLYGON ((110.9652 28.99895… |
| Zhijiang | 92069 | 112587 | POLYGON ((109.8818 27.60661… |
| Lengshuijiang | 43258 | 107515 | POLYGON ((111.5307 27.81472… |
| Shuangfeng | 144567 | 162322 | POLYGON ((112.263 27.70421,… |
| Xinhua | 132119 | 145517 | POLYGON ((111.3345 28.19642… |
| Chengbu | 51694 | 61826 | POLYGON ((110.4455 26.69317… |
| Dongan | 59024 | 79925 | POLYGON ((111.4531 26.86812… |
| Dongkou | 69349 | 82589 | POLYGON ((110.6622 27.37305… |
| Longhui | 73780 | 83352 | POLYGON ((110.985 27.65983,… |
| Shaodong | 94651 | 119897 | POLYGON ((111.9054 27.40254… |
| Suining | 100680 | 116749 | POLYGON ((110.389 27.10006,… |
| Wugang | 69398 | 81510 | POLYGON ((110.9878 27.03345… |
| Xinning | 52798 | 63530 | POLYGON ((111.0736 26.84627… |
| Xinshao | 140472 | 151986 | POLYGON ((111.6013 27.58275… |
| Shaoshan | 118623 | 174193 | POLYGON ((112.5391 27.97742… |
| Xiangxiang | 180933 | 210294 | POLYGON ((112.4549 28.05783… |
| Baojing | 82798 | 97361 | POLYGON ((109.7015 28.82844… |
| Fenghuang | 83090 | 96472 | POLYGON ((109.5239 28.19206… |
| Guzhang | 97356 | 108936 | POLYGON ((109.8968 28.74034… |
| Huayuan | 59482 | 79819 | POLYGON ((109.5647 28.61712… |
| Jishou | 77334 | 108871 | POLYGON ((109.8375 28.4696,… |
| Longshan | 38777 | 48531 | POLYGON ((109.6337 29.62521… |
| Luxi | 111463 | 128935 | POLYGON ((110.1067 28.41835… |
| Yongshun | 74715 | 84305 | POLYGON ((110.0003 29.29499… |
| Anhua | 174391 | 188958 | POLYGON ((111.6034 28.63716… |
| Nan | 150558 | 171869 | POLYGON ((112.3232 29.46074… |
| Yuanjiang | 122144 | 148402 | POLYGON ((112.4391 29.1791,… |
| Jianghua | 68012 | 83813 | POLYGON ((111.6461 25.29661… |
| Lanshan | 84575 | 104663 | POLYGON ((112.2286 25.61123… |
| Ningyuan | 143045 | 155742 | POLYGON ((112.0715 26.09892… |
| Shuangpai | 51394 | 73336 | POLYGON ((111.8864 26.11957… |
| Xintian | 98279 | 112705 | POLYGON ((112.2578 26.0796,… |
| Huarong | 47671 | 78084 | POLYGON ((112.9242 29.69134… |
| Linxiang | 26360 | 58257 | POLYGON ((113.5502 29.67418… |
| Miluo | 236917 | 279414 | POLYGON ((112.9902 29.02139… |
| Pingjiang | 220631 | 237883 | POLYGON ((113.8436 29.06152… |
| Xiangyin | 185290 | 219273 | POLYGON ((112.9173 28.98264… |
| Cili | 64640 | 83354 | POLYGON ((110.8822 29.69017… |
| Chaling | 70046 | 90124 | POLYGON ((113.7666 27.10573… |
| Liling | 126971 | 168462 | POLYGON ((113.5673 27.94346… |
| Yanling | 144693 | 165714 | POLYGON ((113.9292 26.6154,… |
| You | 129404 | 165668 | POLYGON ((113.5879 27.41324… |
| Zhuzhou | 284074 | 311663 | POLYGON ((113.2493 28.02411… |
| Sangzhi | 112268 | 126892 | POLYGON ((110.556 29.40543,… |
| Yueyang | 203611 | 229971 | POLYGON ((113.343 29.61064,… |
| Qiyang | 145238 | 165876 | POLYGON ((111.5563 26.81318… |
| Taojiang | 251536 | 271045 | POLYGON ((112.0508 28.67265… |
| Shaoyang | 108078 | 117731 | POLYGON ((111.5013 27.30207… |
| Lianyuan | 238300 | 256646 | POLYGON ((111.6789 28.02946… |
| Hongjiang | 108870 | 126603 | POLYGON ((110.1441 27.47513… |
| Hengyang | 108085 | 127467 | POLYGON ((112.7144 26.98613… |
| Guiyang | 262835 | 295688 | POLYGON ((113.0811 26.04963… |
| Changsha | 248182 | 336838 | POLYGON ((112.9421 28.03722… |
| Taoyuan | 244850 | 267729 | POLYGON ((112.0612 29.32855… |
| Xiangtan | 404456 | 431516 | POLYGON ((113.0426 27.8942,… |
| Dao | 67608 | 85667 | POLYGON ((111.498 25.81679,… |
| Jiangyong | 33860 | 51028 | POLYGON ((111.3659 25.39472… |
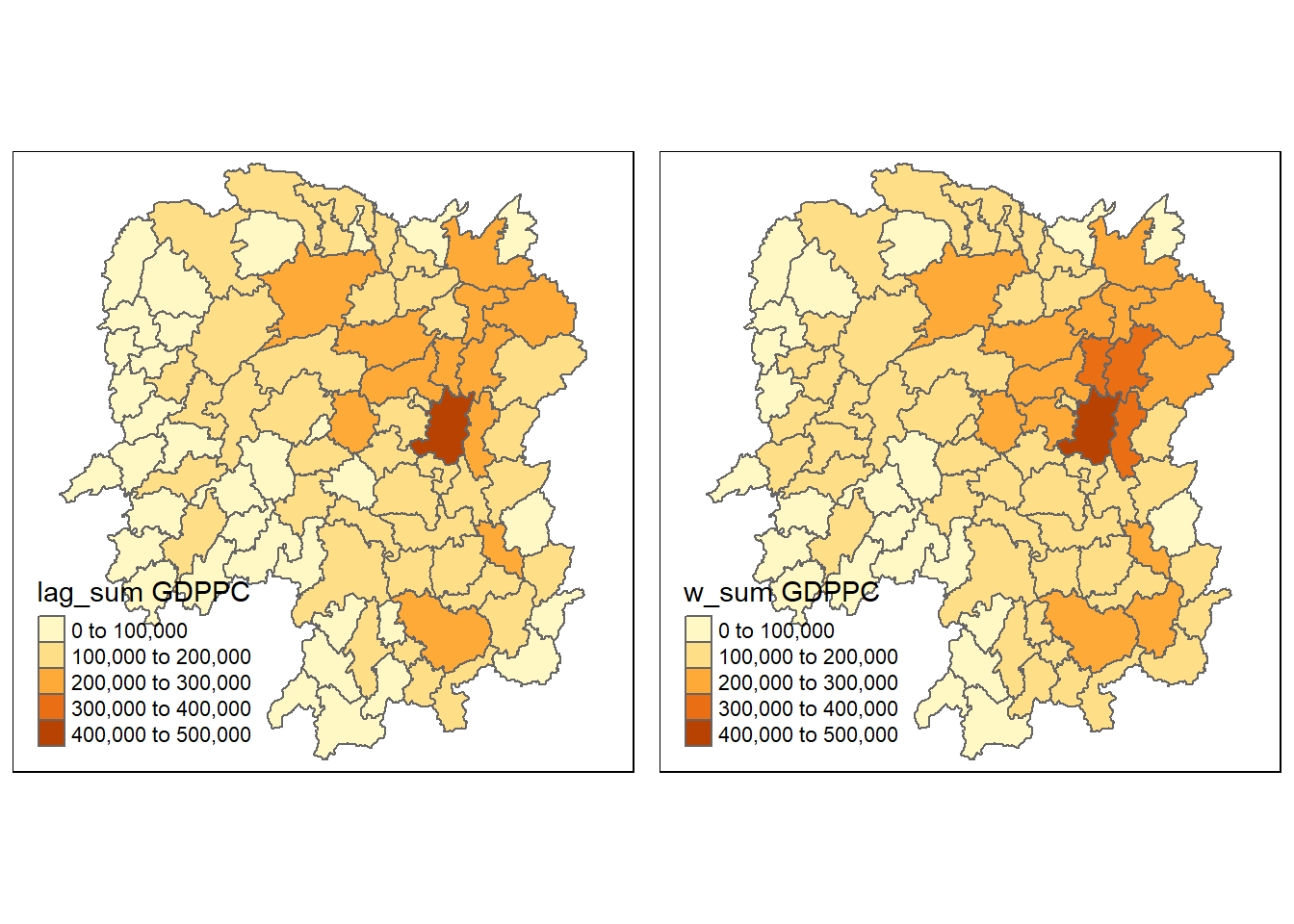
Lastly, we can draw plots to compare the two methods: Spatial Lag as a Sum of Neighboring Values and Spatial Window Sum
w_sum_gdppc <- qtm(hunan, 'w_sum GDPPC')
tmap_arrange(lag_sum_gdppc, w_sum_gdppc, asp = 1, ncol = 2)